Introduction - Rule framework
It’s designed for automating accounting, data cleaning, and rule-based updates safely and transparently.
Glossary
|
Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Rule |
A JSON definition that describes what to find and what to update. |
|
Condition |
A logical statement used to match rows (e.g., “where description contains ‘fuel’”). |
|
Actor |
Defines the action taken when a rule’s conditions match (e.g., update, assign value). |
|
Static Value |
Fixed replacement for a column (e.g., set |
|
Column Copy |
Uses data from another column within the same row. |
|
Table Lookup |
Fetches a value from another table (e.g., find GL account by name). |
|
xRule |
A versioned rule reference with context (jurisdiction, entity type). |
|
xMappingTable |
Layered rule mapping across versions and company scopes. |
|
Company Scope |
Restricts rules to a specific company_id; defaults to global fallback. |
|
Global Rule |
Base rule applied across all companies unless overridden. |
|
Audit Log |
Record of all input data, rules applied, and output changes. |
|
Mutation History |
The before/after snapshots of updated rows. |
|
Force Mode |
Optional override to process beyond default row limits. |
|
Idempotency |
Ensures a rule applied twice has the same end result (no duplication). |
|
Persistence Layer |
Stores final booking or journal entries post-rule execution. |
|
GL Account (General Ledger) |
Accounting entry category (e.g., Sales Revenue, Bank Fees). |
|
IBAN Counterparty |
The external account identifier used to infer transaction category or GL mapping. |
|
Invoice Line Item |
Each detailed item in an invoice, used for VAT or cost allocation. |
|
VAT Rule |
Defines how to calculate tax based on jurisdiction, product, or invoice type. |
Core Actions
|
Endpoint |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Finds rows matching your filters |
|
|
Updates matched rows based on a rule (“actor”) |
All changes are logged for audit and can be undone.
Concepts
|
Term |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
resource_table |
The table you want to work on |
|
conditions |
Filters that describe which rows to select |
|
actor |
Defines what to change and where the new value comes from |
|
mutation history |
Every update is logged for safety and traceability |
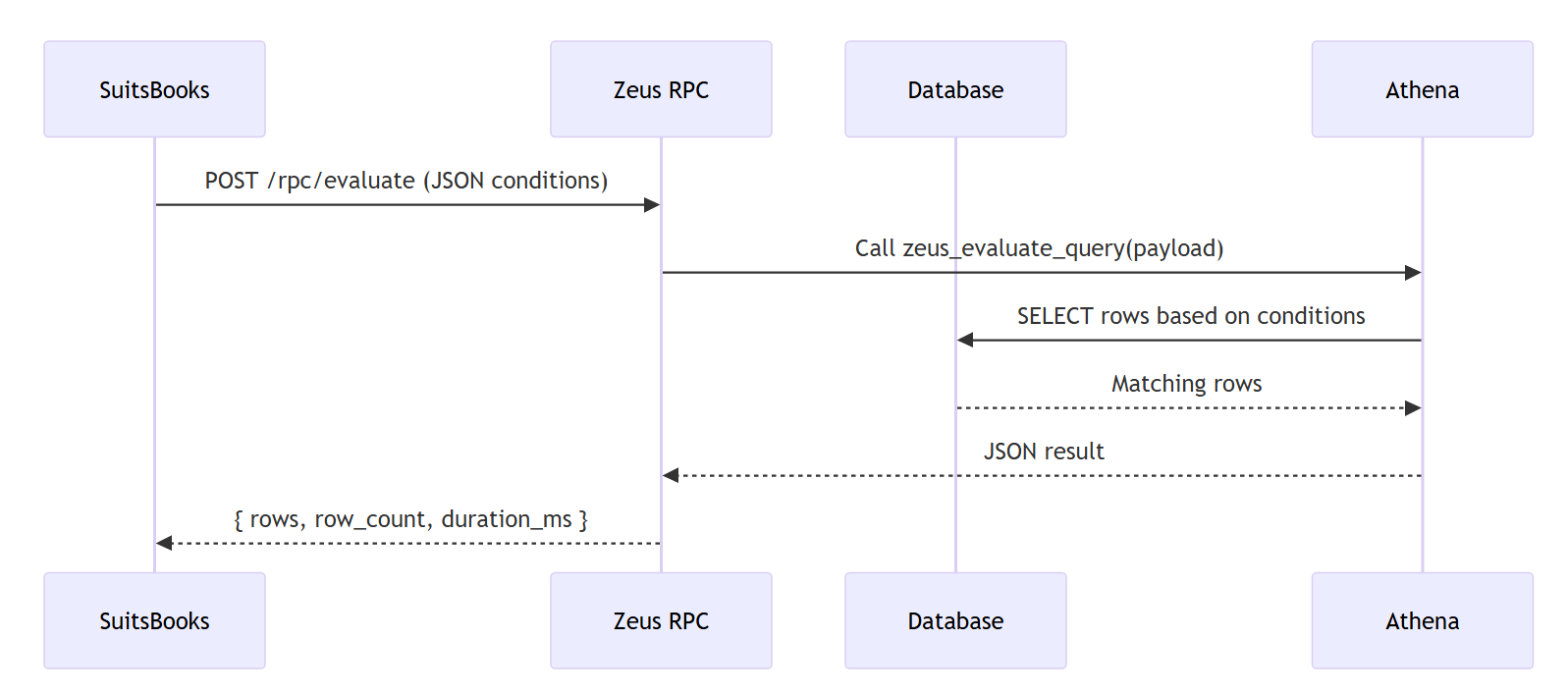
Evaluation pipeline
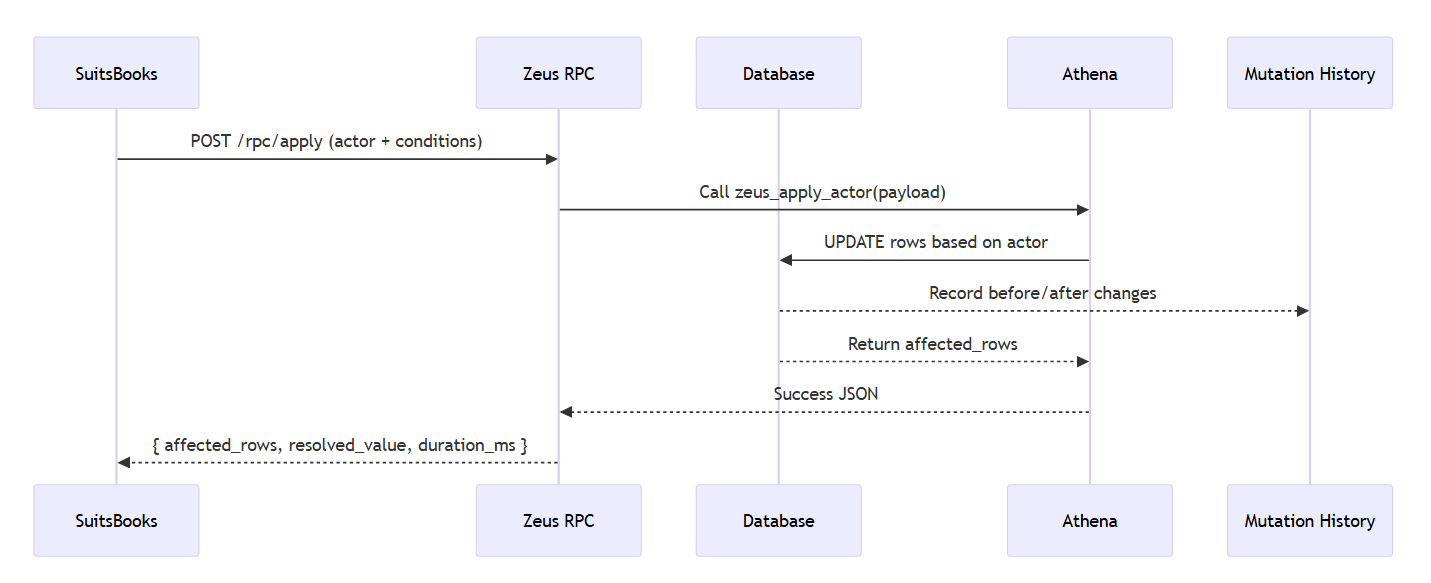
Mutation pipeline
WIP: Transformation pipeline
This is still in progres, it will be a late child before or after the Mutation or Evaluation, to allow more leniency and non-perfect values like the closest match with several algorithms;
-
Levensteihns distance
Pipeline Summary
-
Input — Financial or transactional data (banks, APIs, CSVs).
-
Schema Validation — Ensures the data format matches expected structure.
-
Normalization — Cleans, renames, or standardizes columns.
-
Rule Resolution — Finds which rule applies (xRule + xMappingTable).
-
Evaluation Engine — Applies rules considering date, country, and entity.
-
Booking Generator — Creates accounting entries and VAT splits.
-
Persistence — Saves data with audit logs and supports undo/redo.
-
Events — Triggers cache invalidation or downstream updates.
xRule architecture
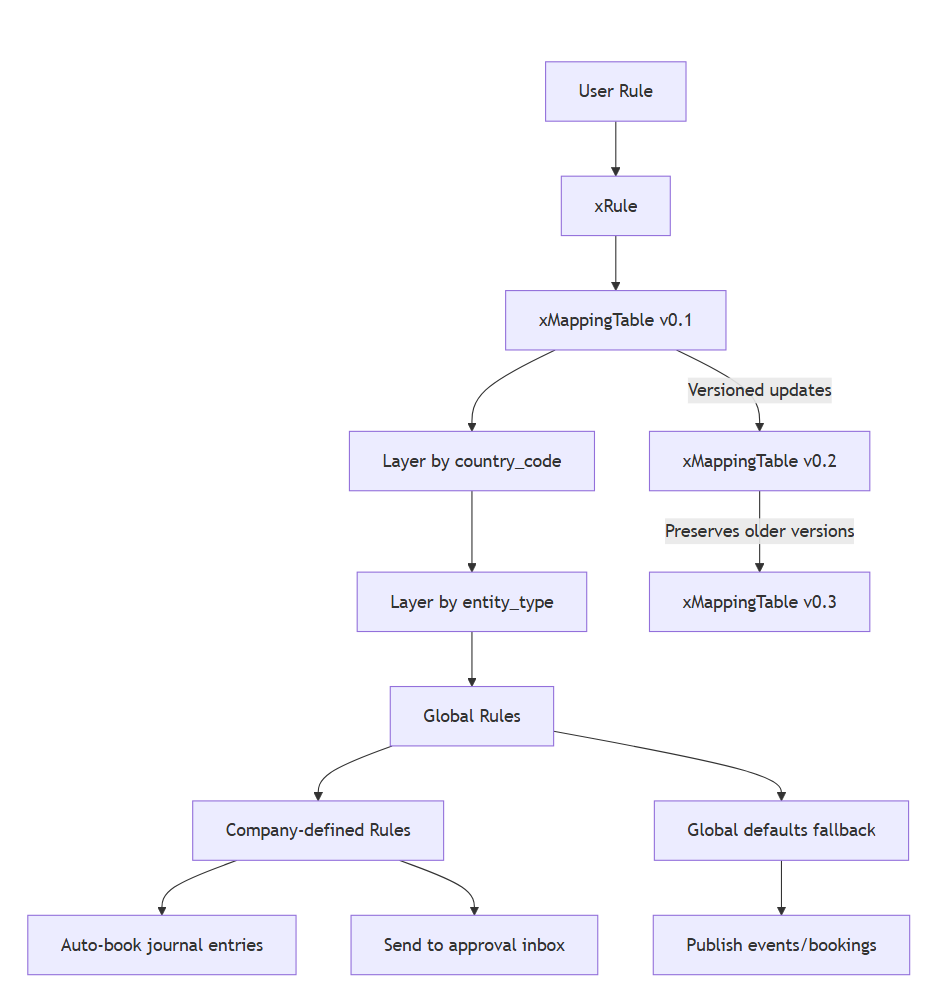
Explanation
-
Every User Rule becomes an xRule, linked through a versioned mapping table.
-
The xMappingTable handles:
-
Country-level layering (
country_code) -
Entity-level layering (
entity_type)
-
-
Global mappings apply first; company rules override last.
-
Each mapping version (v0.1 → v0.2 → v0.3) is time-bound, so changes in tax laws or logic don’t retroactively affect old data.
Multi-tenancy support
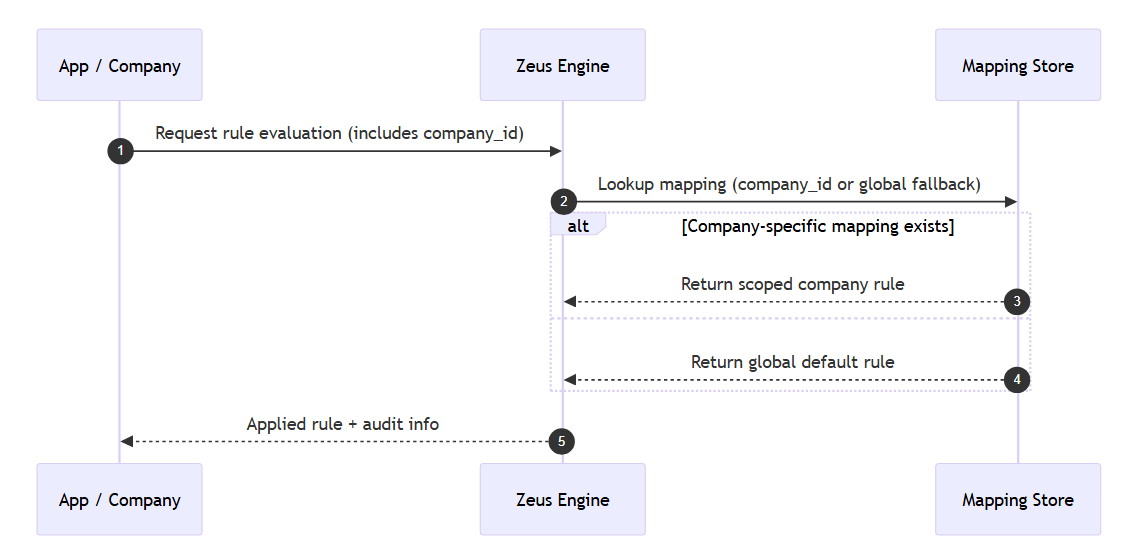
Key Concepts
-
Rules and mappings are scoped by
company_id. -
If no company-specific mapping exists, Zeus falls back to global rules.
-
All inputs, rule IDs, and outputs are audited and versioned.
Example 1: Mapping + VAT Over Time
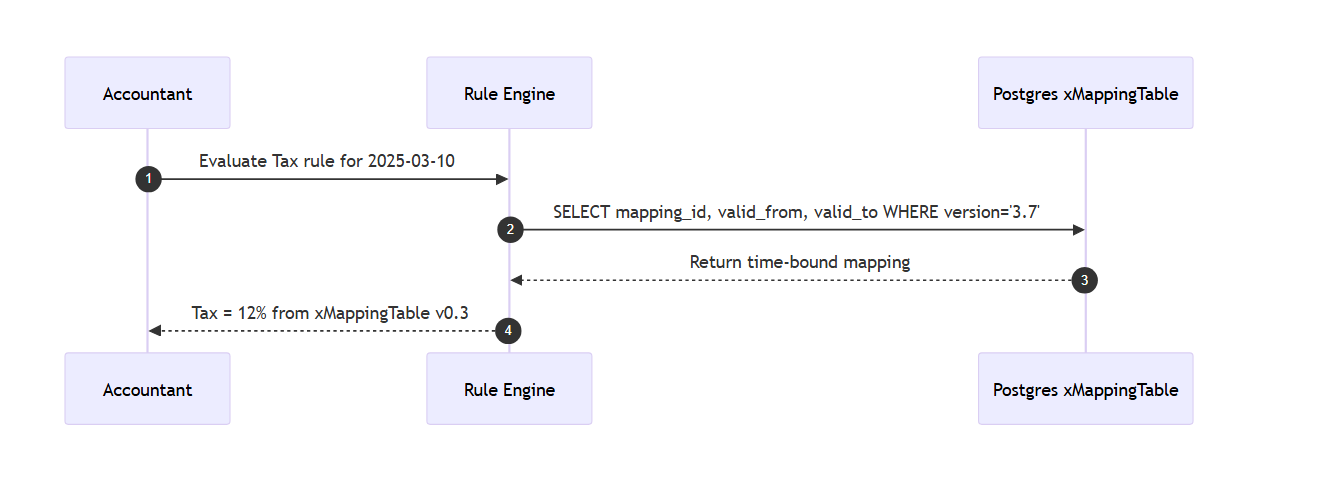
Explanation
-
Rules are versioned historically, allowing correct re-evaluation over time.
-
e.g. Tax 2020 = 10%, 2021 = 11%, 2022 = 12%
-
-
Each mapping version stays intact for archival and prevents reprocessing old data incorrectly.
Audit & Publishing flow
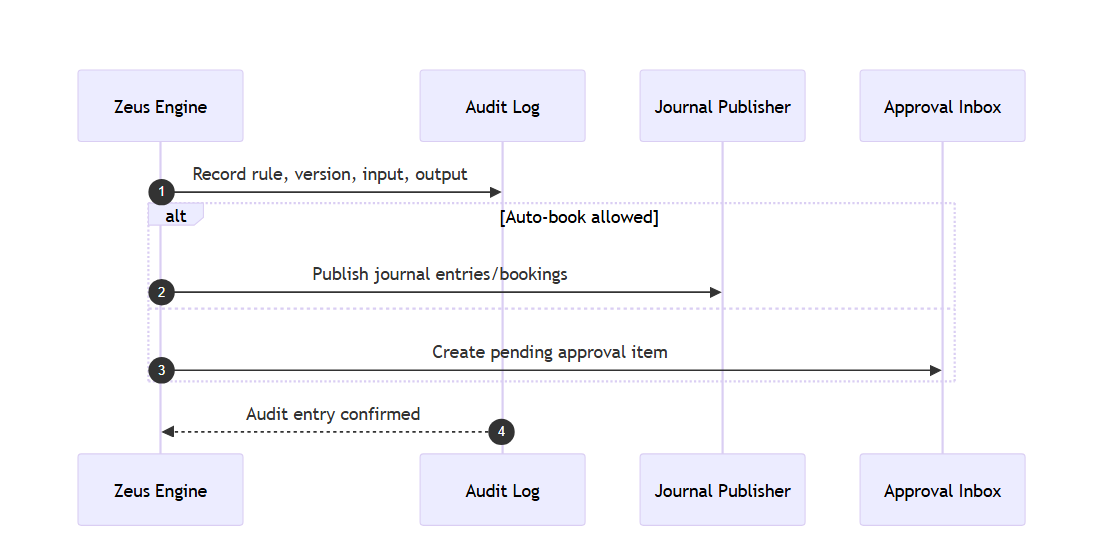
Outcome Options
-
Auto-book: The rule executes directly and books entries.
-
Approval required: The rule output waits for manual confirmation.
Execution flow
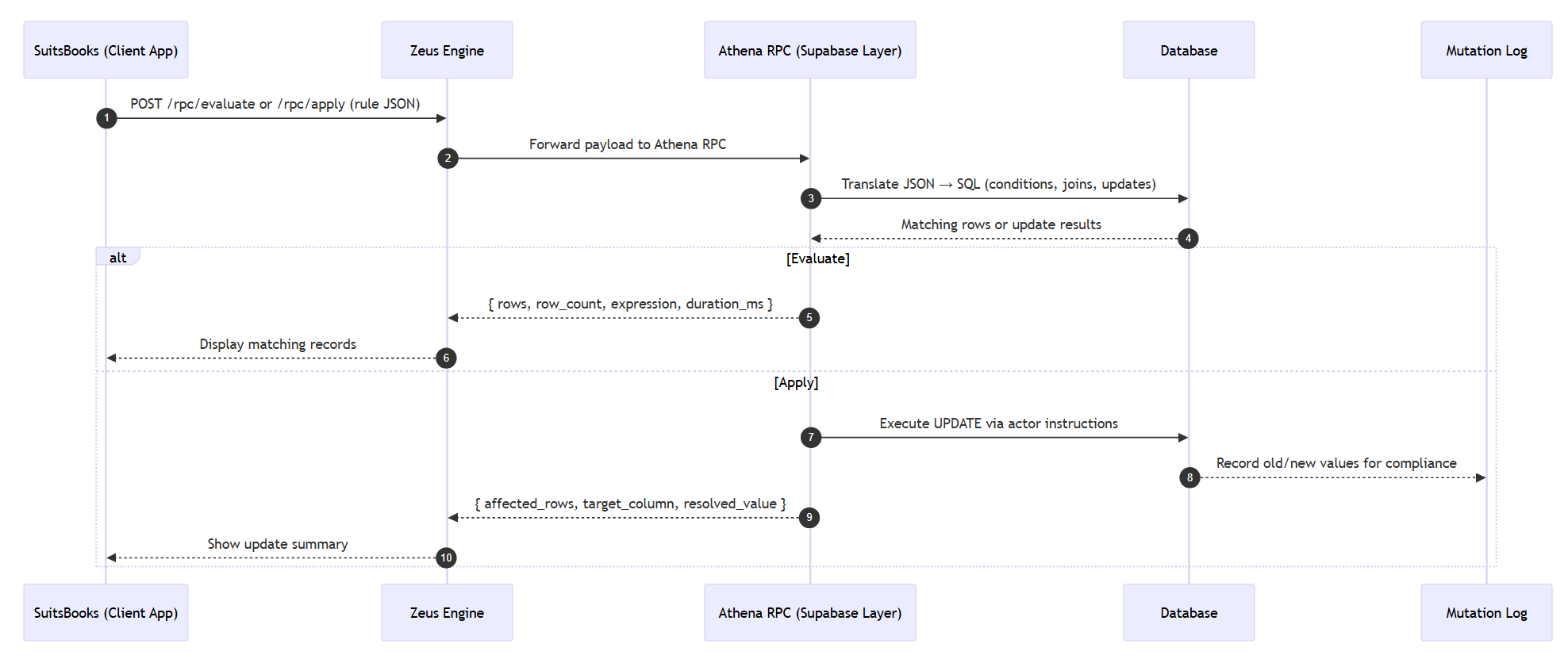
Expression operators
|
Operator |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Equal |
|
|
Not equal |
|
|
Greater than |
|
|
Greater or equal |
|
|
Less than |
|
|
Less or equal |
|
|
Case-sensitive pattern match |
|
|
Case-insensitive pattern match |
|
|
Value exists in array/list |
|
|
Column value is NULL |
|
|
Column value is not NULL |
Rule Structure
Each rule defines:
|
Field |
Purpose |
Datatype |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Which company the rule applies to |
|
|
|
The table being queried or updated |
|
|
|
Filters that determine which rows match |
See aforementioned *1 |
|
|
The operation to apply (update instructions) |
See aforementioned *2 |
|
|
Maximum rows per execution |
|
|
|
Whether to override row safety limits |
|
Rule Logic Breakdown
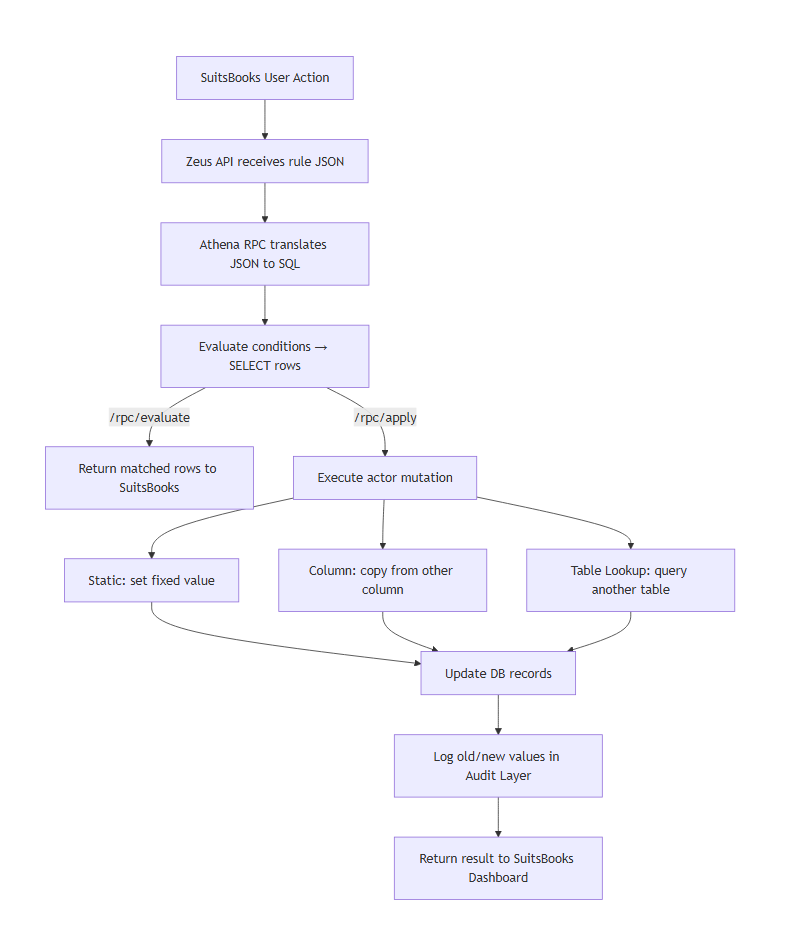
How is a rule applied in practice
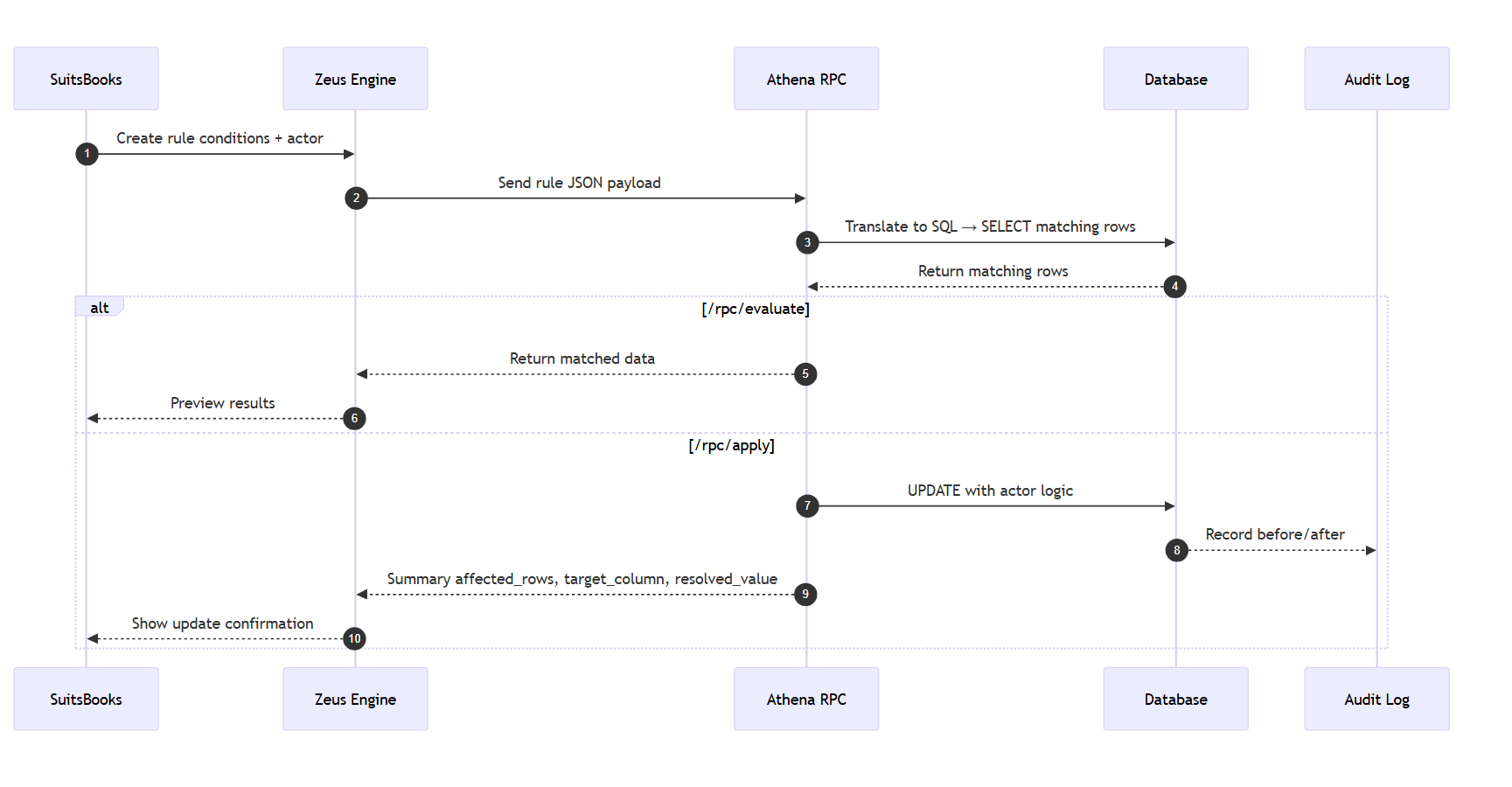
Safety Features
-
Allowlist: Only permitted tables can be edited.
-
Row limit: Caps the number of affected rows.
-
Force mode: Add
"force": trueto override the limit (use carefully). -
Audit trail: Logs every before/after change for undo and inspection.
|
Variable |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Connects Zeus to |
— |
|
|
Schema where Zeus runs |
|
|
|
List of allowed tables per company |
|
|
|
Maximum number of rows per operation |
|
Example case studies
-
Tag transactions that mention “fuel”
-
Fill missing categories from another column
-
Set GL accounts automatically from lookup tables
-
Automatically calculate VAT for invoice line items
Case 1 : VAT Calculation (Rule-Based)
Goal: Automatically calculate and update VAT for invoice line items.
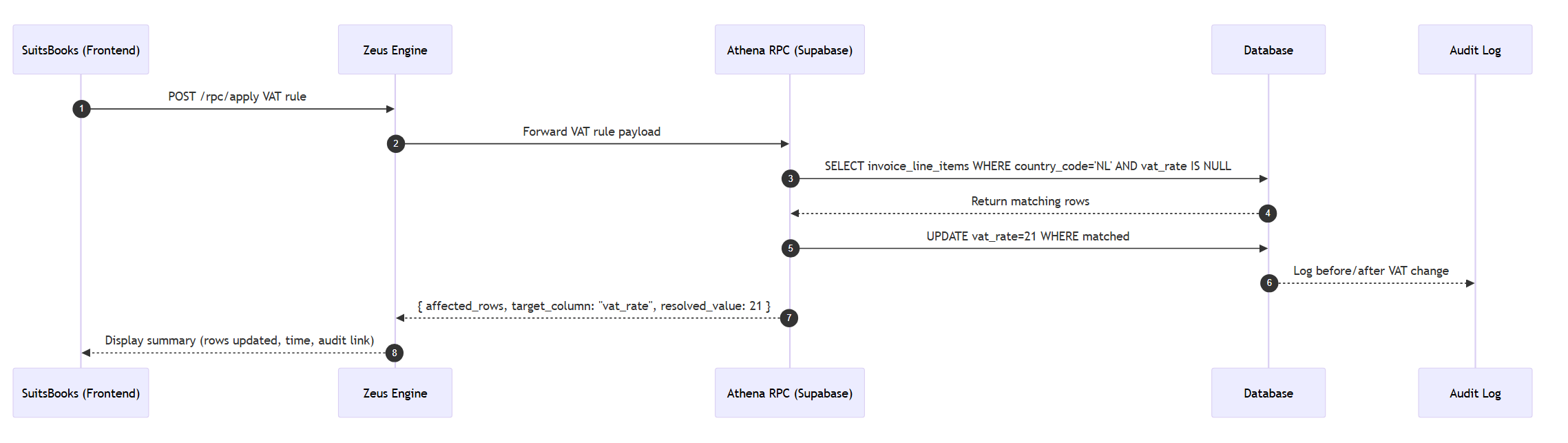
Result: All Dutch invoice lines without VAT get vat_rate = 21.
Obviously we start to see where the culprit starts to develop caveats, not all line items that are dutch are 21%, but we will get into just that.
|
Product Type |
VAT Rate |
|---|---|
|
Consulting |
21 |
|
Software |
21 |
Case 2: Assigning RGS Codes as Ledgers to Dutch bank accounts
Goal: Ensure each Dutch bank account always maps to a unique, fixed RGS code ledger (e.g., 11000, 11001, etc.).
The same IBAN must always receive the same RGS code, even across rule re-runs or migrations.
Conditions:
-
Country code must be
NL. -
Each IBAN gets a stable RGS code from the
rgs_mappingstable. -
Once assigned, it is locked — cannot be overwritten unless force-updated.
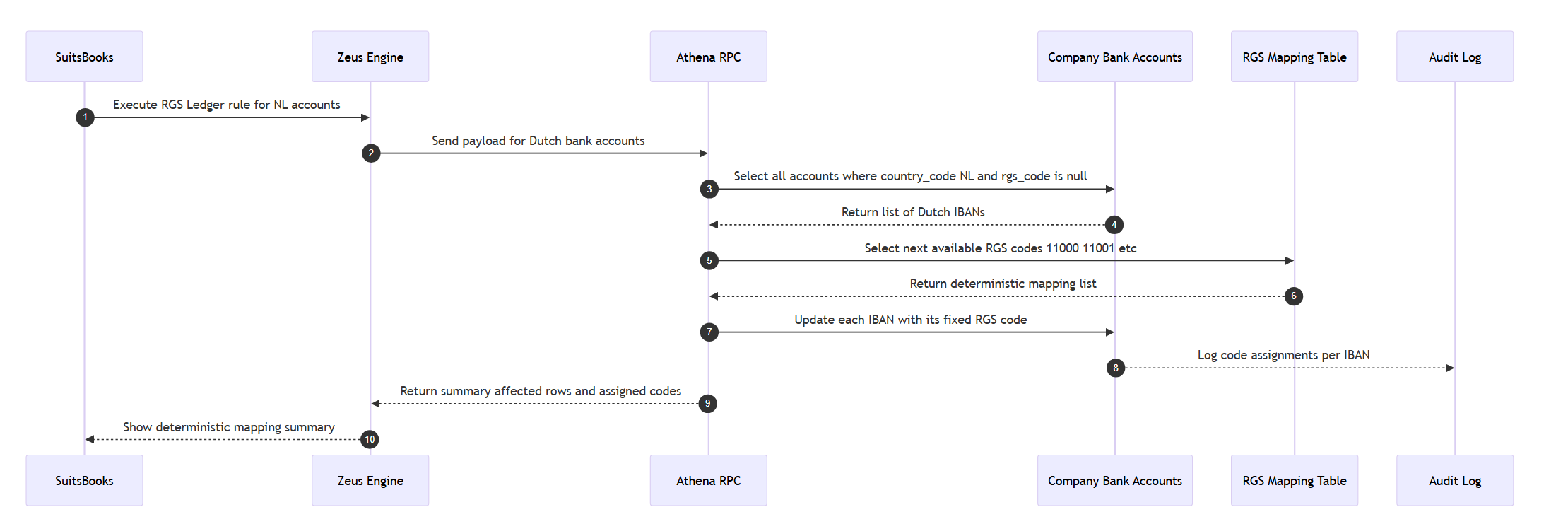
Result:
Example output in SuitsBooks
|
IBAN |
Country code |
RGS Code |
Locked |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NL55ABNA0123456789 |
NL |
11000 |
True |
Always 11000 for this IBAN |
|
NL22INGB0001234567 |
NL |
11001 |
True |
Always 11001 for this IBAN |
|
NL03RABO0004567890 |
NL |
11002 |
True |
Always 11002 for this IBAN |
Each subsequent IBAN is assigned the next sequential ledger code (11000 + n).
If re-run, Zeus checks audit history and reuses the same code — ensuring permanent ledger consistency.
Behavior summary
|
Action |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Sequential Assignment |
New Dutch accounts get the next unused RGS code (e.g., 11000, 11001). |
|
Deterministic |
Same IBAN always gets the same RGS code. |
|
Locked |
Once assigned, cannot be changed without |
|
Audited |
Each change logged with IBAN, timestamp, and assigned code. |
|
Idempotent |
Running the rule again does not alter existing mappings. |
Case 3: GL Account assignment (based on IBAN Counterparty)
Goal: Assign correct GL account to transactions based on counterparty IBAN.
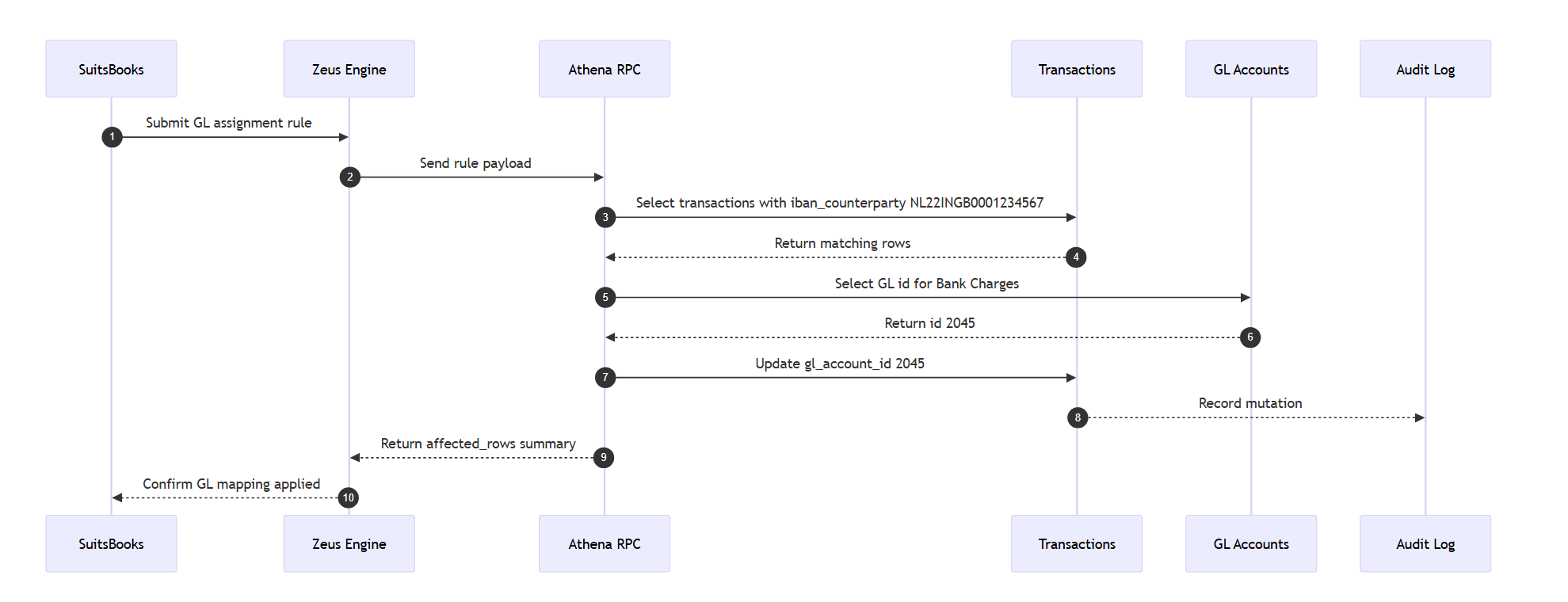
Result:
|
Transaction ID |
IBAN |
GL Account |
|---|---|---|
|
TX-100 |
NL22INGB0001234567 |
Bank Charges |
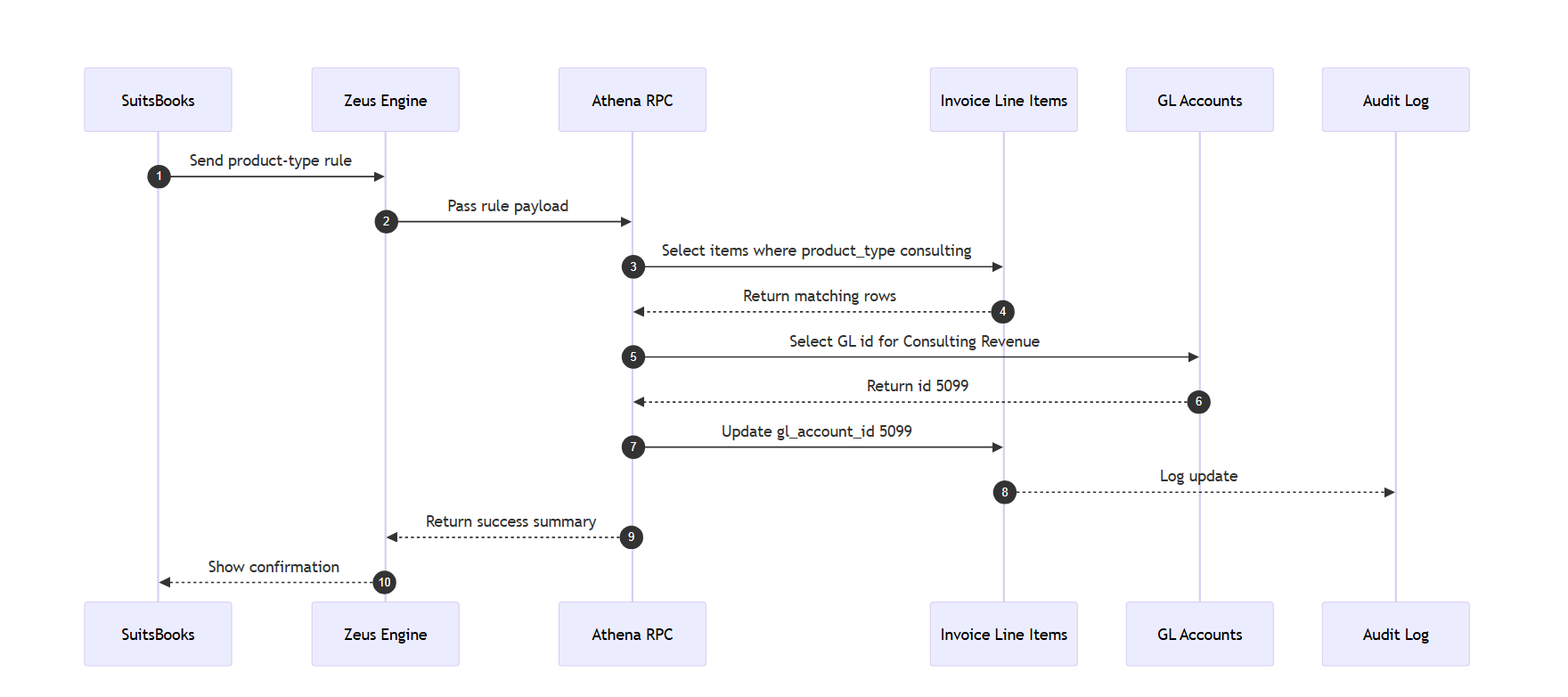
Case 4: GL Account Assignment (Invoice Line Items)
Goal: Link consulting products to “Consulting Revenue” GL account
Case 5: Debit and Credit Assignment
Goal: Determine debit or credit automatically based on transaction type.
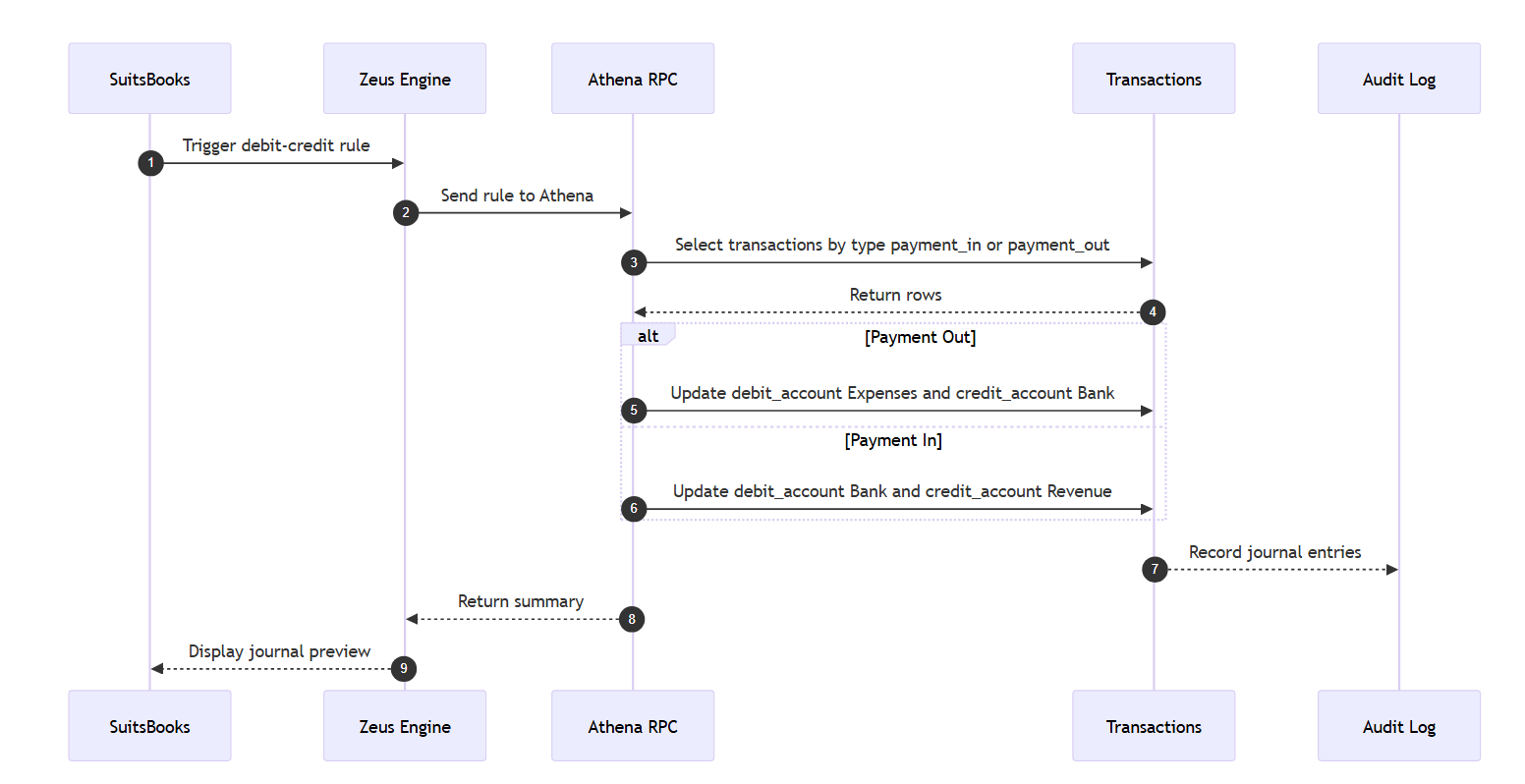
Result:
|
Transaction |
Type |
Debit |
Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
|
TX-200 |
Payment Out |
Expenses |
Bank |
|
TX-201 |
Payment In |
Bank |
Revenue |
Case 6: VAT Exceptions for Dutch Products
Goal: Handle multiple VAT rates (9% or 21%) depending on product type.
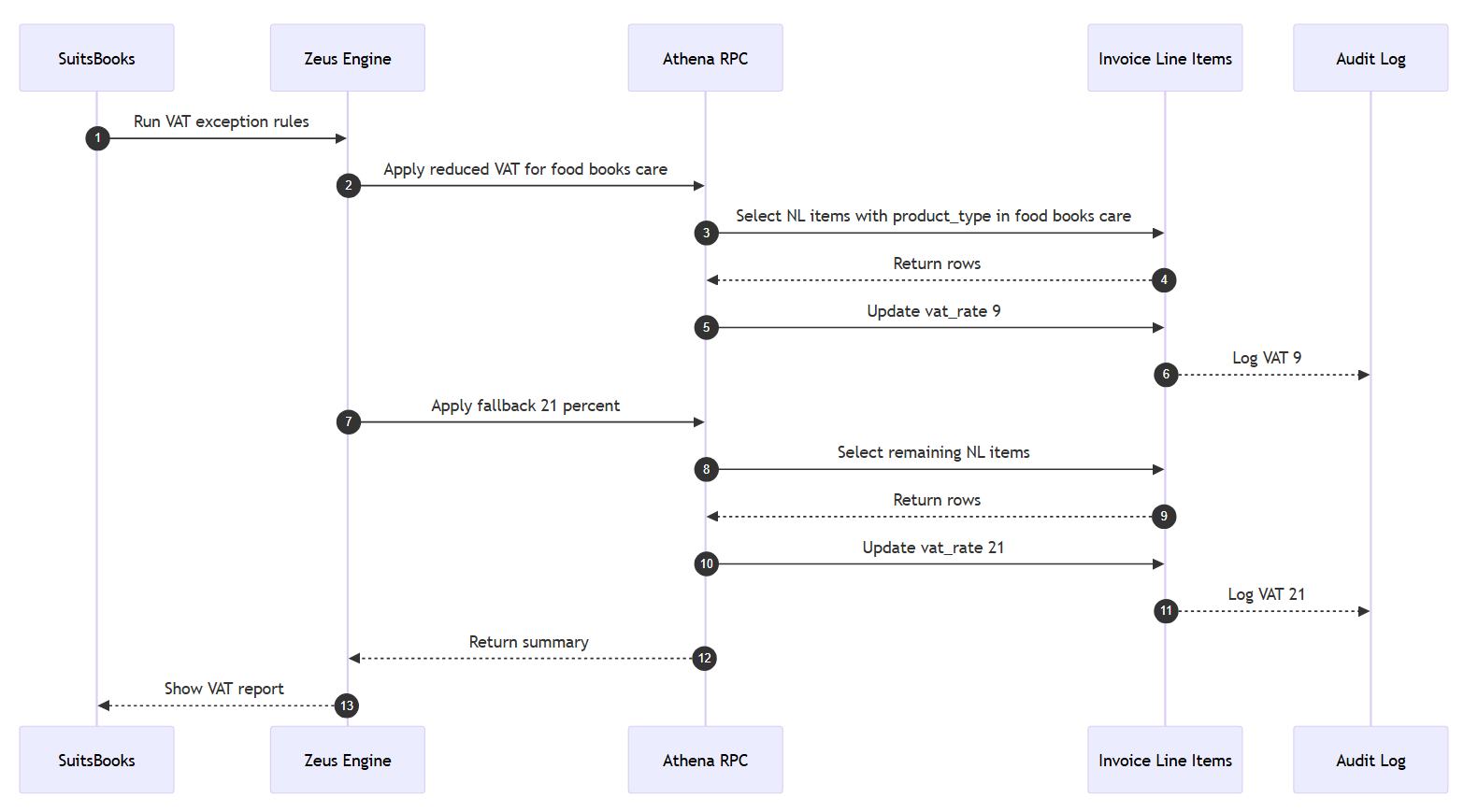
Result:
|
Product Type |
VAT Rate |
|---|---|
|
Food |
9% |
|
Books |
9% |
|
Care |
9% |
|
Consulting |
21 |
Case 7: Combined VAT and RGS Workflow
Goal: Apply VAT rules first, then assign RGS codes in the same batch.
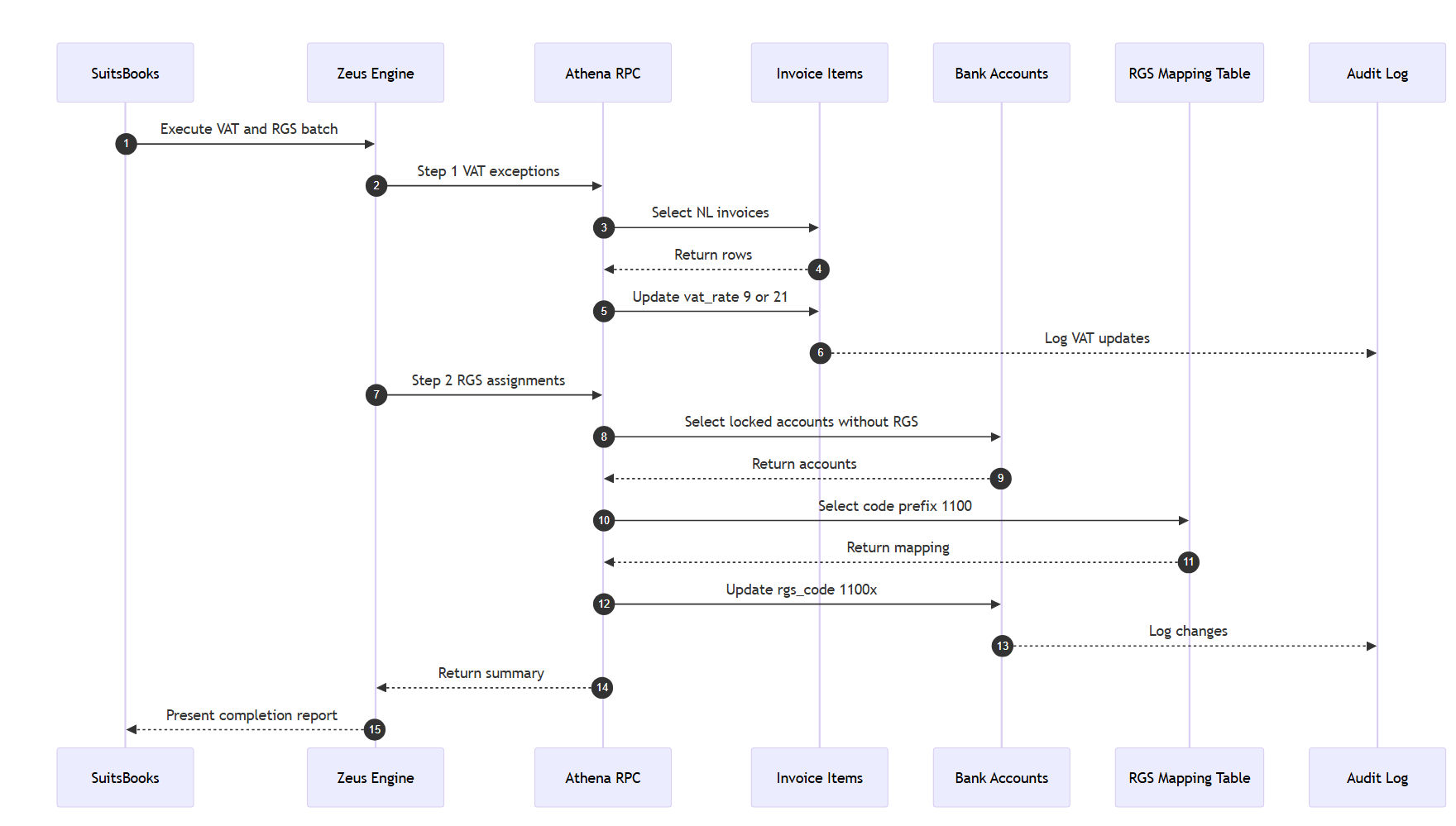
Result:
|
Step |
Operation |
Rows |
Output |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
VAT Update |
125 |
9 or 21 |
|
2 |
RGS Mapping |
3 |
1100x |